This is a PLC Ladder Logic to calculate the flow rate and also count the total flow or totalizer.
Flow Meter Totalizer
By using some math, bit and comparator functions, prepare a PLC program that can calculate the flow rate of gas and also count the total flow.
Problem Solution:
To calculate flow, first we have to measure differential pressure.
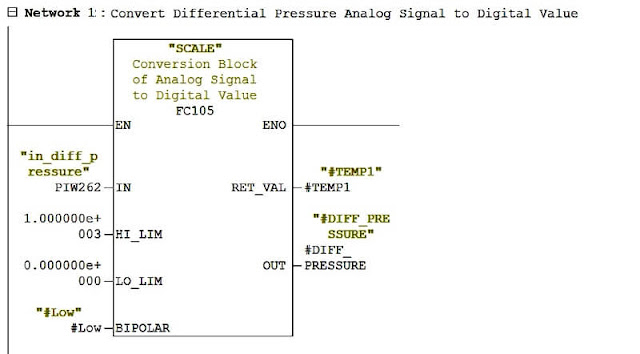
To measure differential pressure, Differential Pressure transmitter installed at pipe line.
Range of DP transmitter is 0-1000 Pa.
Output of this transmitter is in standard electrical signal which is 4-20 mA. Convert this signal into digital signal by connecting transmitter to AI module of PLC.
To find the Flow Rate, Apply formula ( Flow Rate = k √∆P ) given by the designer using math block in PLC.
Prepare a logic for Flow totalizer using math function in PLC.
NOTE :
In this example, we are assuming the transmitter output 4-20 mA is equivalent to “Differential Pressure” instead of direct flow reading. So we are applying the square root function in PLC to derive the equivalent flow rate from this measured “differential pressure”.
PLC Address & Data Types
PLC Ladder Logic
Network 1 :







Comments
Post a Comment