Control panel is used to accommodate instruments for the purpose of measurement, monitoring, protection, detection, control and manage the processes.
The panels are located in a control room as well as a field termed as a local control panel (LCP) for operational convenience.
Table of contents
Control Panel
Types of Control Panels
Flat Control Panel
Breakfront Panel
Console
Control Panel
The control panels are designed based on the type of energy and dynamics associated. Panels are named based on a functional media such as electrical, electronic, air, and oil.
- The panel is called PLC control panel with a PLC installed, associated wiring, power supplies.
- If the panel is Pneumatic controller/ Indicators which are operated by air is called pneumatic control panel with associated controllers, transducers gauges, etc.,
- If a panel is called hydraulic, if it is operated by oil with associated pressure gauges, directional control valves, etc.,
The modern industry uses instruments for the management of various parameters such as electrical (voltage, current, power) process temperature, pressure, flow, acceleration, density, level mass, volume compositions.
The electronic instrument panels are needed to be placed away from high switch noise-producing elements such as VFD, motors, and pumps. Signal noise effects the measurement.
Types of Control Panels
- There are three basic types of control panels.
- Flat Control Panels
- Breakfront Control Panels
- Console type Control Panels
The dimensions of a particular panel type are as per the suitability of the application.
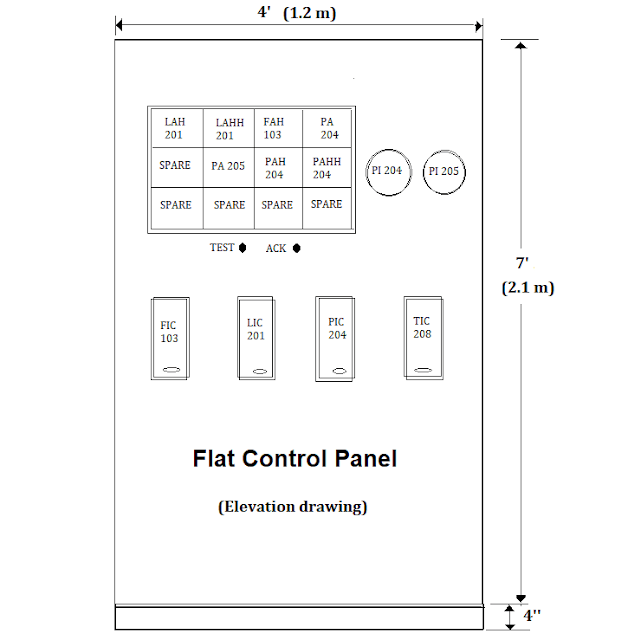
Flat Control Panel
The flat control panel is the least expensive and easiest to construct and simple design of all types.
The straight and vertical plane of the panel allows an orderly layout of tubing, electrical ductwork, and miscellaneous equipment.
Instruments can be arranged as per the operator’s convenience and requirement. Flat control panels are best suitable for PLC/DCS system installation.
Breakfront Panel
Breakfront panels allow greater use of the front plane of the board.
The top portion of the panel is swung downwards to an angle normal to the line of sight allowing better visibility.
Console
The Console appears to be eye-catching and very pleasing to most people.




Comments
Post a Comment