This article is about the programming of two-hand control used in the press industry.
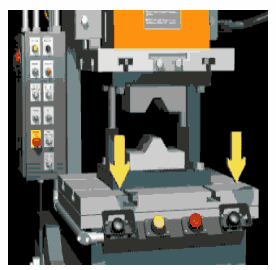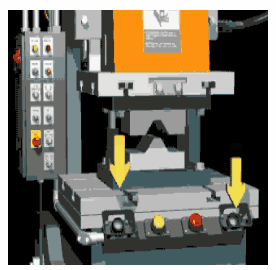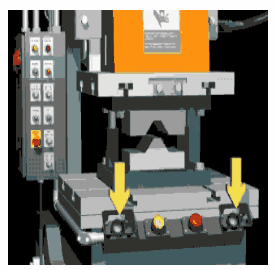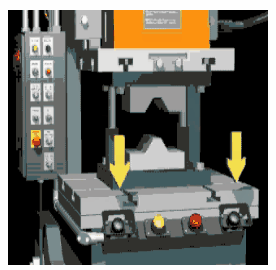
The purpose of this program is about safety to prevent fatal accidents. Below is an image of how the press machine looks and why we care about safety. As you can see there are pushbuttons used to control the press machine. The center plate is pushed against the surface of the workpiece when we press the push buttons.
The two pushbuttons must be pressed at the same time to operate the press machine as shown in the below animation.
When the operator uses his one hand to press the button and use his second hand when plate pushing against the surface, he can injure himself. The powerful force of pushing a plate can easily squeeze hands if the operator tries to maneuver things in a hurry.
Below I have explained the program used to prevent such incidents with the help of Siemens TIA Portal.
Here in the below figure press machine which has two inputs and one output is shown. Inputs are connected to the plc digital input (DI) module and single output which is connected to the digital output (DO) module.
Below is a list of inputs and outputs used for the program.
Inputs:
- Push Button (PB_1): I0.0
- Push Button (PB_2): I0.2
Outputs:
- Press Machine Output: Q0.0
Two-Hand Control Logic
Logic Description
Network 1:
Here two push-buttons PB_1 & PB_2 are connected in series. When both push-buttons are pressed at the same time, then the signal will pass through NC contact of timer T0 and energize the output.
Network 2:
Now if any single push button either PB_1 or PB_2 is pressed then timer T0 on-delay timer (S_ODT) is energized, here in our case after 5 seconds.
Here NC contact of press machine’s output is also used after push button because if the output is ON then it won’t allow the timer to energize.
So, the machine’s output will only energize when both buttons are pressed together.

Comments
Post a Comment