In this article, we will learn about the information you can get from the resources tab of the Siemens PLC.
Resources as the name indicate it contains all the information related to the PLC program.
Let’s take a software tour and find out where the resources tab is and what it contains.
Here, I will show you in the both TIA PORTAL and the Simatic manager.
Resources Tab in Siemens PLC
Let’s first open TIA PORTAL. Enter into the programming environment.
On the left side select the CPU and do right-click on it. From the list choose “call structure”.
The following window will appear. On the right side in the corner, you can see the “resources” tab.
Click on it.
As you can see in the below window in the resources tab you can have detailed information of the used and unused I/Os, CPU memory, and memory space consumed by programming and data blocks.
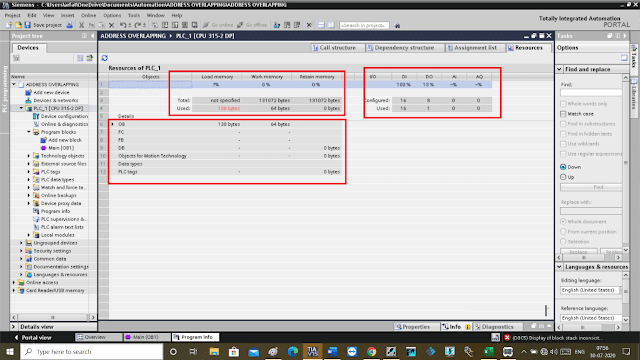
In the CPU memory, you can see the amount of the used and remaining memory. The same way you can access all the information about the programming and data blocks.
In the input and output section, you can see the information on the number of inputs and outputs you have configured for the project.
You can also see the used input and output section. This is a piece of really very helpful information to have as an automation engineer.
This can be helpful while implementing a new control system or installing a new machine.
To access the same information using Simatic manager first open it. Go to the programming environment.
However, in Simatic manager, it won’t have a specific tab to check resources but you can see memory space as shown in the below window.
Click on “module information”.
The following window will appear. Click on the memory section and you have information about memory space used by the program.
In this tab, you have access to lots of information about the PLC program.





Comments
Post a Comment