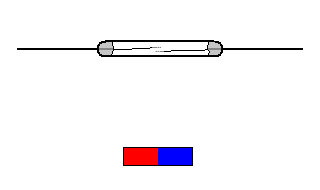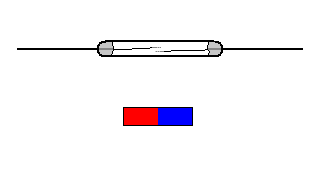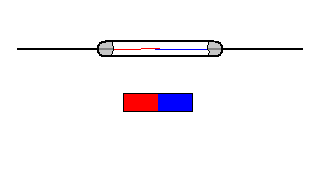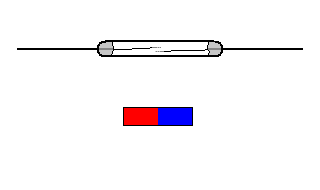
The reed switch is an electrical switch operated by an applied magnetic field. It was invented at Bell Telephone Laboratories in 1936 by W. B. Ellwood.
It consists of a pair of contacts on ferrous metal reeds in a hermetically sealed glass envelope. The contacts may be normally open, closing when a magnetic field is present, or normally closed and opening when a magnetic field is applied.
The switch may be actuated by a coil, making a reed relay, or by bringing a magnet near to the switch. Once the magnet is pulled away from the switch, the reed switch will go back to its original position.
Reed switches Animation :
Reed switches Operation:
The simplest magnetic-field sensor is a reed switch. It contains two ferromagnetic nickel and iron reed elements in an evacuated, hermetically sealed glass tube to minimize contact arcing.
When an axially aligned magnet approaches the switch, its magnetic force closes the reeds. The magnet typically generates at least a 50 Gauss force to overcome the return force or spring of the reed elements.
Reed switches are inexpensive, require no standby power, and can function with both ac and dc electrical loads. However, they are relatively slow, so they may not respond fast enough for some high-speed applications.
Since the switches are mechanical devices with moving parts, they have a finite number of operating cycles before they eventually fail. Switching high-current loads can further reduce life expectancy.
Also, low-cost reed switches occasionally deliver unwanted, multiple switching points as the twin lobes of certain magnets pass by.


Comments
Post a Comment