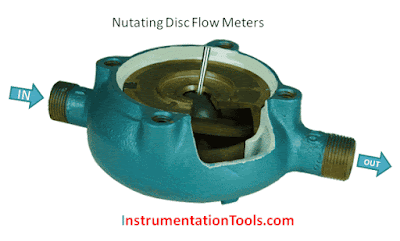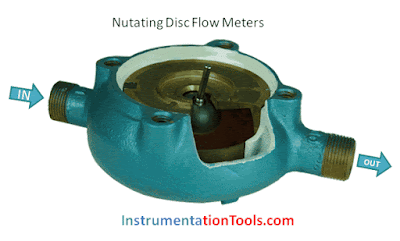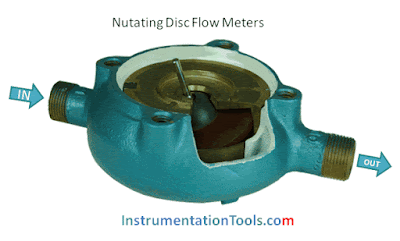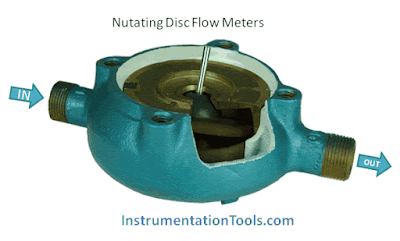
Nutating disc flow meters are one of the most common types of positive displacement flow meter. They operate by having a disc mounted to a central ball. When fluid enters the chamber, it causes the disc to wobble (nutate), transferring the displaced volume to the register.
Something to keep in mind, is that due to the nutating discs nature, the accuracy of this type of flow meter can be adversely affected by fluctuations in liquid viscosity.
Nutating Disc Flow Meters
Liquid enters a precision-machined chamber containing a disc which nutates (wobbles). The position of the disc divides the chamber into compartments containing an exact volume. Liquid pressure drives the disc to wobble and a roller cam causes the nutating disc to make a complete cycle.
This motion is translated into rotary motion by means of a ball and shaft, which is attached to the disc. The movements of the disc are transmitted by gear train to an indicator/totalizer or pulse transmitter.
There are inherently more leakage paths in this design and it tends to be used where longer flow meter life is required rather than high performance; however, close clearances between the disc and chamber ensure minimum leakage for accurate and repeatable measure of each volume cycle.
A disc attached to a sphere is mounted inside a spherical chamber. As fluid flows through the chamber, the disc and sphere unit nutates. The nutation causes a pin, mounted on the sphere perpendicular to the disc, to rock.
Each revolution of the pin indicates a fixed volume of liquid has passed. A mechanical or electromagnetic sensor detects the rocking of the pin and the flow is measured.
How Sensor Picks up the reading –
These flow meters may use a Hall sensor to sense the rotation and the same was converted into equivalent flow.
Also Read: How Hall Sensor Works ?
Advantages of Nutating Disc Flow Meters:
*May be constructed from a variety of materials.
*High accuracy and repeatability.
Disadvantages of Nutating Disc Flow Meters:
*Accuracy is adversely affected by viscosities below the meter’s designated threshold.


You have provided excellent stuff in this article. I'm glad I came into this page because it has a lot of useful information about roxtec mct installation manual. Thank you for sharing this article.
ReplyDeleteThis is a splendid website! I"m extremely content with the remarks!. 50kv capacitors
ReplyDelete