Mass spectrometer :
Principle:
Mass spectrometer works on mass to charge ratio principle.
To know the Mass spectrometer, first we have to know what is Mass Number ?
Mass number is also called atomic mass number which is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atomic nucleus.
As carbon (C) has 6 protons and 6 neutrons so in carbon total mass number is (6+6 =12)
As CH4 (Methane) total mass is
Carbon mass is 12 and H mass is 1 then total mass is = 12+1 x 4 = 16
Mass to charge ratio is denoted by m/z or m/e, Mass to charge ratio of a cation is equal to mass of cation divided by charge of cation. Charge of cation in mass spectrometer is always +1. So mass-to-charge ratio of a cation is usually equal to the mass of the cation.
A mass spectrometer is a gas analyzer in which sample molecules are pulled into a vacuum system then ionized (using an electrical charge), which are then separated by mass-to-charge ratio by the quadrupole and the detector measures the equivalent ion current (quantitative) which is the analyzer output reading.
Parts of Mass Spectrometer:
Here we are discussing about Extrel Make, MAX 300 Model Mass Spectrometer
Inlet and outlet valves:
There are two rotary selector valves in which one rotary selector valve is used for sample gas and 2nd is used for calibration.
Each rotary valve has 16 ports each port has a separate outlet and there is a common outlet. In calibration, rotary selector valve outlet is plugged to avoid the mixing of gases.
At one time, only one inlet is connected with common port and left port is connected to outlet and its continuous vent. By continuous vent sample become dry and there is no deposition of condensate. The Inlet ports with the larger diameter fitting, contains a 2 micron filter and are labeled with an arrow pointing towards the valve body. The Inlets are in the row closest to the common port for both the front loading and rear loading valves.
After the outlet of common parts, there are 2 types of inlets used.
Direct inlet
*Differentially pumped inlet
*The direct inlet is required for samples near 1atm and the differentially pumped inlet is used for low pressure applications.
After this sample goes in Ionizer

Ionizer main parts :
Filaments: filament is a part of the ionizer assembly. A filament is simply a resistor to which electrical power is applied and converted to heat the filaments. The filament’s temperature will rise until it loses free electrons at the rate the heat is generated. There are 2 filaments. One is always in line and second always is in auto made when first is fail then second automatic comes in line.
The main purpose of a filament is to produce free electrons (e–) which will then collide with a neutral atom in the ion volume to produce ions.
Lens: A unique voltage is applied to each of the lens elements, as they help focus the positively charged ions toward the Quadrupole and the detector. The ions, which have a positive charge, are attracted to a negative charge that is applied to a lens and repelled by a positive charge.
How ionizer works: A current is continuously applied to the (active) filament to heat it up and emit electrons. The capillary leaks a small amount of sample into the ionizer where it is bombarded by electrons to make positively charged ions. The positive charged ions are attracted towards the lens stack where there is a negative voltage potential. The ions are pulled out of the ionizer and directed into the quadrupole mass filter

Quadrupoles: The main heart of mass spectrometer is Quadrupoles. Quadrupoles are known as the “Mass Filter. , they are four ¾ inch (19mm) stainless steel rods held together by two ceramic collars. The quadrupole separate ions according to their mass per charge ratio (m/z). They deflect and attract the ions by an applied magnetic field, produced by voltages applied to the quadrupole. The voltage applied to the quads changes continuously, which attracts and deflects each ion equally toward the detector If a positive voltage is applied to one set of rods and a negative voltage to the other set of rods, the rods with the negative voltage will attract the positive ions. Eventually, the ions will hit the negatively charged rods and become neutralized. The ion becomes neutralized when it collides with the negative rod, because the rod gives up an electron to the ion.
Summary Of Quadrupole working
*RF and DC voltage is applied to opposite rods
*Only ions of the right mass make it all the way down the quad
*Other masses are unstable and will strike the quad and be neutralized and pumped away
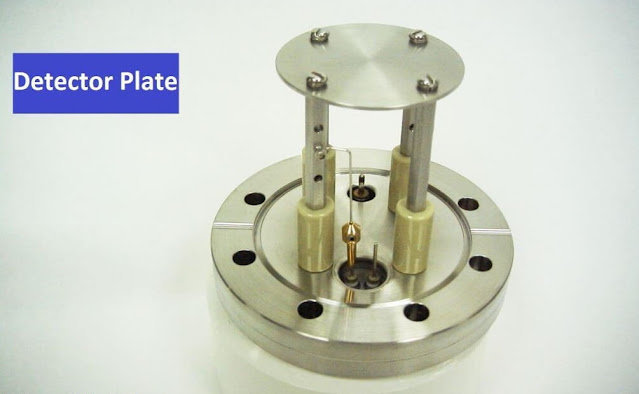
Detector: For detection the positively charged ion we use a faraday plate. The faraday plate is a stainless steel flat disk on which ions are detected. After exiting the quadrupole, the positively charged ion will strike the stainless steel plate, producing a small current which is proportional to the gas concentration .that is sent to the preamplifier.
Vacuum Pump: Vacuum pump is used for pump out the collide or neutralized ions from quadrupole its outlet is connected with venting system.





Comments
Post a Comment