The Cable type Float Level Switch is made from chemical resistant polypropylene. It is durable, low-cost,and specially designed to assist with long range and multiple point level detection in liquids. It is also suitable for tanks containing pumps and granular solutions.
The Cable Float Level Switch is a structured by using either micro switches, proximity switches or reed switches to control the contact. It’s user-friendly design is ideal for level measurement.
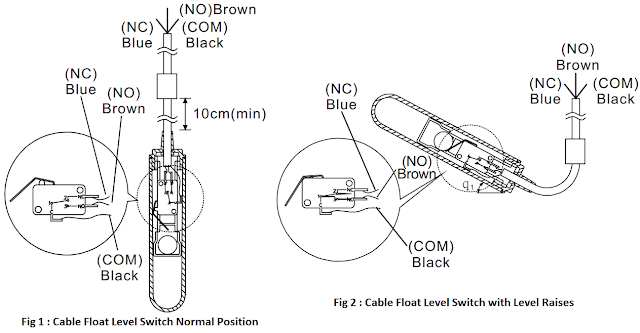
The switches will transmit an ON or OFF contact signal output when the float rises and turns upwards. The switch contains a metal ball that can slide as the float position changes. The change in contact signal is used to detect the level.
Cable Float Level Switch using Micro Switch
When the float hasn’t contacted the liquid, the blue and black wires are in an open state and the contact mode will be NC.
When the liquid level rises and lifts the float until it reaches the actuation angle, the brown and black wires will be in an open state and the contact mode will be NO.


Comments
Post a Comment