Ammonia gas detector working principle and calibration. (Make: Dragger Model : Polytron 5100)
Gas detector is a very important safety device for any chemical plant. Its can give information in any small leak from any pipelines and with early action we can save any incident in plant.
In any chemical plant generally we use four types detector:
Hydrocarbon Detector
CO detector
NH3 detector
Chlorine detector
Here we discussed about Ammonia detector.
Principle :
Ammonia detector works on electrochemical principle. Electrochemical sensors are electrochemical measuring transducers for measuring the partial pressure of gases under atmospheric conditions. The ambient air being monitored diffuses through a membrane into the liquid electrolyte in the sensor. The electrolyte contains a measuring electrode, a counter-electrode and a reference electrode. An electronic potentiostatic circuit ensures a constant electrical voltage between the measuring electrode and reference electrode.
Voltage, electrolyte and electrode material are selected to suit the gas being monitored so that it is transformed electrochemically on the measuring electrode and a current flows through the sensor. This current is proportional to the gas concentration. At the same time, oxygen from the ambient air reacts at the counter-electrode electrochemically. The current flowing through the sensor is amplified electronically, digitized and corrected for several parameters (e.g. the ambient temperature). The resulting measured value is given as an analog, 4-20 mA signal.
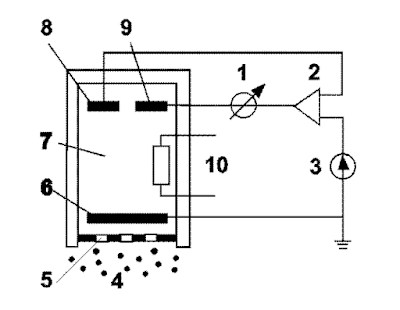
Gas Detector Parts :
1.Meter
2.Potentiostat
3.Direct current supply
4.Measured gas
5.Membrane
6.Measuring electrode
7.Electrolyte
8.Reference electrode
9.Counter electrode
10.Temperature sensor
Configuration of Gas Detector:
Gas detector can be used as a two wire or as three wire device.
Connect the gas detector wiring as per your requirement & Power ON the detector. Display shows a start up timer.
Wait for the timer to complete and then press down navigation and go to FSD for Span range.
Calibration of Gas Detector:
For calibration we use N2 gas for zero calibration and 90 PPM ammonia cylinder for span gas .
Typical Calibration Setup :
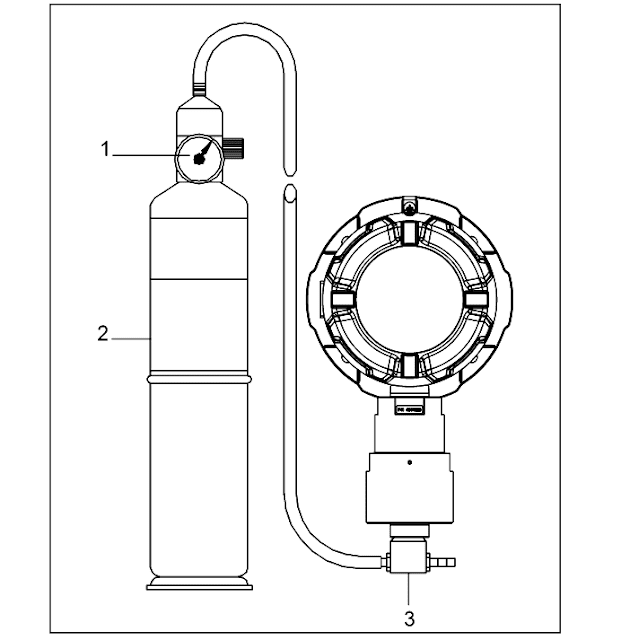
Parts :
1.Regulator
2.Calibration gas cylinders ( Zero Gas Cylinder & Span Gas Cylinder )
3.Calibration adapter
For zero calibration
1.Connect the regulator with N2 cylinder adapter to detector then adjust the flow to 0.5 l/min
2.Press down navigation key for 5 sec its showing -0- Adj.
3.Tap [OK].
4.The display will show the current value blinking.
5.Wait for the value to stabilize.
6.Use [UP] / [DOWN] navigation to adjust the value to 0.
7.Enter [OK] then detector return to main menu.
8.Turn off gas flow and remove the calibration adapter from the sensor or disconnect tubing.
Note : Ambient air can be used to zero the sensor instead of nitrogen or Zero Air if the area is known to be free of the target gas or any gas to which the sensor may be cross-sensitive. In this case, no cylinder or calibration adapter is needed for the zero calibration.
For span calibration
1.Connect the regulator with 90 PPM ammonia cylinder adapter to detector then adjust the flow to 0.5 l/min
2.Press down navigation key for 5 sec its showing -0- Adj. press down its showing SPn Adj
3.Tap [OK].
4.The display will show the current value blinking.
5.Wait for the value to stabilize.
6.Use [UP] / [DOWN] navigation to adjust the value (As mention on cylinder certificate, means span cylinder gas concentration).
7.Enter [OK] then detector return to main menu.
8.Turn off gas flow and remove the calibration adapter from the sensor or disconnect tubing.
General Preventive Maintenance : In every 6 months once, carry out the calibration of gas detector.
Reference : Drager Manual



Comments
Post a Comment