A Programmable Logic Controller, or PLC, is a ruggedized computer used for industrial automation. These controllers can automate a specific process, machine function, or even an entire production line.
How does a PLC work?
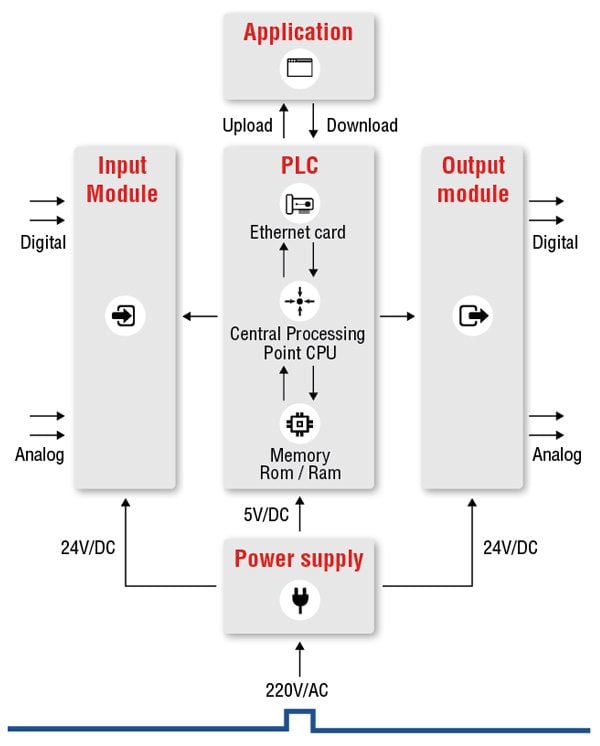
The PLC receives information from connected sensors or input devices, processes the data, and triggers outputs based on pre-programmed parameters.
Depending on the inputs and outputs, a PLC can monitor and record run-time data such as machine productivity or operating temperature, automatically start and stop processes, generate alarms if a machine malfunctions, and more. Programmable Logic Controllers are a flexible and robust control solution, adaptable to almost any application.
There are a few key features that set PLCs apart from industrial PCs, microcontrollers, and other industrial control solutions:
• I/O – The PLC’s CPU stores and processes program data, but input and output modules connect the PLC to the rest of the machine; these I/O modules are what provide information to the CPU and trigger specific results. I/O can be either analog or digital; input devices might include sensors, switches, and meters, while outputs might include relays, lights, valves, and drives. Users can mix and match a PLC’s I/O in order to get the right configuration for their application.
• Communications – In addition to input and output devices, a PLC might also need to connect with other kinds of systems; for example, users might want to export application data recorded by the PLC to a supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) system, which monitors multiple connected devices. PLCs offer a range of ports and communication protocols to ensure that the PLC can communicate with these other systems.
• HMI – In order to interact with the PLC in real time, users need an HMI, or Human Machine Interface. These operator interfaces can be simple displays, with a text-readout and keypad, or large touchscreen panels more similar to consumer electronics, but either way, they enable users to review and input information to the PLC in real time.
Advanced PLC Features
In today’s world of the Industrial Internet of Things (iIoT), and Industry 4.0 programmable controllers are called upon to communicate data via Web browser, connect to databases via SQL, and even to the cloud data via MQTT.
The All-In-One PLC
An All-in-One PLC integrates the controller with the HMI panel, creating a compact, easy-to-use automation solution. Users no longer need to establish PLC to panel communications and can program both the Ladder Logic and HMI design in a single software environment. An all-in-one approach saves time, reduces wiring, and cuts the cost of purchasing multiple devices.
How is a PLC Programmed
A PLC program is usually written on a computer and then is downloaded to the controller
Most PLC programming software offers programming in Ladder Logic, or “C”. Ladder Logic is the traditional programming language. It mimics circuit diagrams with “rungs” of logic read left to right. Each rung represents a specific action controlled by the PLC, starting with an input or series of inputs (contacts) that result in an output (coil). Because of its visual nature, Ladder Logic can be easier to implement than many other programming languages.
“C” programming is a more recent innovation.
Some PLC manufacturers supply control programming software.
What are the different types of PLC?
In addition to the traditional PLC described above, there are variations, including PLC + HMI controllers.
Programmable Logic Controller by Unitronics
Unitronics is a pioneer in the manufacture and design of Programmable Logic Controllers with integrated HMI panels and built-in I/O. They launched the very first All-in-One PLC on the market and have continued to improve the technology based on market feedback and industry advancements.
Comments
Post a Comment